Setting up and using system components
The control panel of lWindows 7, as it has been done since Windows 98, contains many system mechanisms with which you can control the operation of the operating system, methods and methods of data processing, data protection and encryption systems, the reaction of the operating system to different user actions, etc.
Knowing how these mechanisms work and what they can do, you can effectively manage the computer, which will not only speed up its work, but also make it as easy as possible for you.
CUSTOMIZING THE APPEARANCE
As in previous versions of Windows, the appearance of the Control Panel depends on the display method, which you can change. By default, the view mode is used, in which all mechanisms are grouped into eight categories (Fig. 5.1). Under each category there is a list of elements that are included in it, therefore, in order to select the desired control mechanism, you must first determine in which category it is located, and only by opening the category itself, you can start it.
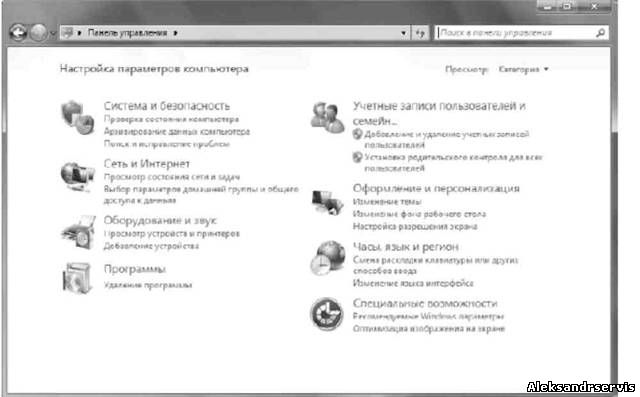
Rice. 5.1. Windows Control Panel in category view
Some people don't like this approach very much, therefore, as in previous versions of the operating system, the developers have provided a view mode in which a list of all mechanisms is displayed in a window without any grouping.
To change the view mode, use the View list in the upper left part of the window. When you click on it, a list of three positions appears: Category, Large icons, Small icons (Fig. 5.2). The last two modes differ only in the size of the icons themselves, which affects the number of icons that are simultaneously displayed in the window. So, if you select the Small icons mode, the maximum number of them will be displayed in the window.
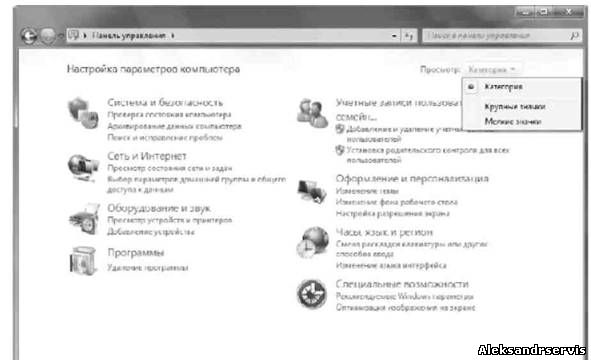
Rice. 5.2. Changing the view mode
In total, there are 45 icons on the Control Panel, each of which is responsible for launching a certain system mechanism, and a short name of the mechanism is displayed next to each icon (Fig. 5.3). Also, if you hover your mouse pointer over an icon for a while, you can see a more complete description of what you can do with this control mechanism.
When mechanisms are launched, additional windows are rarely opened, that is, the same window is used for work, where all the mechanisms of the Control Panel are located. For this reason, navigation between different stages of the selected mechanism is carried out using the arrow buttons, which are located in the upper left part of the window.
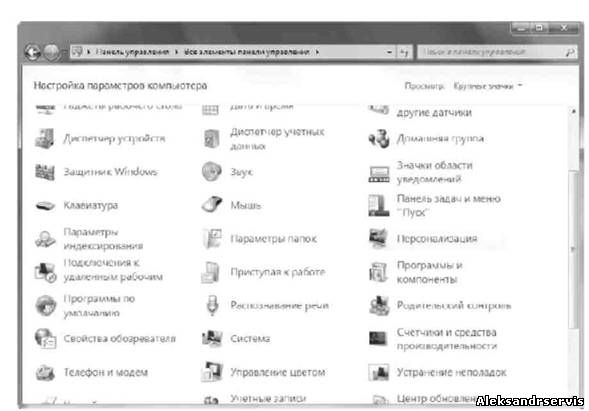
Rice. 5.3. Windows Control Panel in Icon View
5.2. CONTROL PANEL COMPONENTS
As mentioned earlier, the Windows Control Panel contains 45 different
mechanisms with which you can control how the operating system reacts to various
events. Below you will find a description of their capabilities. In addition, in
later chapters of the book, you will learn more about how to configure the main of these
mechanisms, which will allow you to get even more speed and usability from the system
.
Windows Card Space
Windows CardSpace is an identification system developed by Microsoft. Its purpose is to identify a user in any application or on an Internet resource without the need for constant authorization. This allows you to establish secure connections to completely secure resources. The biggest benefit from using this technology is that you don't have to remember the many logins and passwords that you use to register on different resources and use them. Now it is enough to create and configure your account in Windows CardSpace once, and any resource that knows how to use this technology will recognize you as "their own" with all the ensuing consequences.
Using this approach makes it easier to work with important data - bank accounts, payment systems, accounting systems, etc. Since Microsoft guarantees that the data you provide will not “leak” anywhere, it is expected that this technology will be widely adopted as the most advanced technology in existence.
Autorun
Using this system mechanism, you can configure how the operating system reacts to connecting a device. By default, the standard reaction to such events is the appearance of a window with a list of available actions. In the case of manual settings, for example, if there is a video file on the media, you can make it so that when such media is inserted, the video player automatically starts. At the same time, it is possible to configure autorun for different types of media.
Similar settings can be made for connected devices such as USB storage devices.
Administration
This mechanism is prefabricated and contains 14 additional components that are used to administer the operating system. A simple user has nothing to do here, but for a user with administrator rights who is familiar with the basics of administration, the capabilities of these components can be very useful. These components include the following.
□ Windows PowerShell Modules. An improved version of the Command Line utility,
which can be found in the Accessories folder. Using this mechanism, the
computer administrator can control the operation of any device or process running on
computer. For this, the capabilities of scripting programming languages
using the Microsoft .NET Framework technology are used.
d Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. The name speaks for itself. In this mode, Windows Firewall allows you to change a large number of settings related to computer security.
□ iSCSI initiator. A system module that describes a set of rules for how software and connected devices operate using the iSCSI storage system.
□ Data sources (ODBC). Used to configure access to different types of data sources using ODBC technology.
□ System configuration. With this utility, you can manage not only the method of loading the operating system, but also the loading of system services and services, configure the autorun list of programs, etc.
□ Local security policy. The most powerful tool with which you can determine numerous parameters related to the operation of programs and devices. Here you can set up user accounts, various restrictions on working with devices, networks, applications, etc.
□ Task Scheduler. The standard mechanism, which was present in previous versions of the Windows operating system, allows you to add various kinds of scheduled tasks and manage them. With the help of the Task Scheduler, you can set up data copying, reminders of important events, launch various programs, etc.
□ View events. A standard utility that allows you to view the system log of events that constantly occur with programs, the operating system, the security system, etc.
□ System Monitor. A mechanism that can be used to obtain data on the performance of the hardware of the computer, on the use of resources by various processes and applications, as well as to monitor in real time the current consumption of resources and the workload of the main hardware components.
Component Services. With this utility, you can track all software components that are registered in the system. In addition, you can also manage services and view system events here.
Services. With this system mechanism, you can manage all system services that are registered in the operating system. You can start or stop them, customize the way they start, read their descriptions, etc.
Vyts1oyy5 Memory Checker. A utility with which you can start the process of checking the RAM installed on your computer. The check is performed immediately after the computer is restarted and can be performed using three different modes, which differ in the complexity of the tests. After loading the operating system, an icon with a hint will appear in the notification area, in which you can find out the "verdict" of the test.
Computer management. An excellent tool with which you can manage your computer and perform almost all the actions for which the system components described above are used. Since the Manage item is present in the context menu of the Computer icon on the Desktop, this mechanism is the most used by administrators and its convenience cannot be overestimated.
Print management. A mechanism that was not available in previous versions of the operating system. With it, you can manage everything related to printing: ports, printers, etc.
Backup and restore
Any major operating system must have mechanisms in place to quickly back up and restore data or the state of the operating system. Of course, there are such tools in Windows 7.
Using the archiving mechanism, you can always create an archive of the data you need or configure the operating system so that it does this automatically at a specified frequency. Such an opportunity will help protect yourself from a sudden system failure, which can lead to the loss of important data. In this case, you will not find another way to restore the system (not counting, of course, third-party programs).
In addition to creating an archive of certain data, you can also create an archive that includes an image of the entire system, which will allow you to restore all data, including the operating system, if necessary.
Chapter 18 is devoted to working with the Backup and Restore mechanism, its capabilities, subtleties and settings.
Windows Firewall
Windows Firewall is a feature introduced in Windows XP. Its main task is to protect the computer from possible attacks. It does not matter what caused them: the local network, the Internet or the software used. In Windows 7, this tool has incorporated all the best from its predecessors and is now a powerful mechanism that allows you to control the launch of programs that require a connection to the "outside world", determine how to alert and monitor various critical processes, configure system security policies, and much more. other.
Recovery
This tool allows you to restore the operating system. For this, previously created system restore points, disk images, and saved data can be used. As a last resort, you can also reinstall the operating system and then restore the data.
Desktop gadgets
As mentioned above, gadgets are small programs whose window size allows them to be placed on the desktop without much infringement of the rights of other applications.
Gadgets can have different purposes, for example, they can be used to find out the weather forecast, currency quotes, the current time, play mini-games, etc.
Using the Desktop Gadgets mechanism, you can customize the gadgets that are currently displayed on the Desktop, remove or add new ones, change the window size, etc.
Chapter 9 is devoted to configuring and using gadgets.
Date and time
A standard system component that allows you to control the built-in Windows clock , which you can see in the notification bar. In addition, you can set the display of an additional clock, which can show the time in a different time zone. Here you can also configure the synchronization of the computer time with the time of any Internet server, the addresses of which you can add, change or delete yourself.
Location sensor and other sensors
One of the innovations of Windows 7. Allows you to manage a variety of sensors connected to a computer, or sensors that are software-based. Sensor data can be used by any programs that have access to such information, which, in turn, is determined by the security settings.
Device Manager
As with earlier Windows operating systems, the Device Manager component is used to display and configure the hardware that is currently installed on the computer and used by the operating system. Here you can manage drivers, enable or disable devices, configure the resources they use, remove devices from the system, and more.
Credential Manager
It is a repository of information about any of your accounts, including Windows accounts. Here you can add credentials for websites, set up certificate authentication, and more.
HomeGroup
New in Windows 7, you can easily create a HomeGroup and manage how new users join the group. This allows you to create a network between all computers connected to the group and organize full access to shared network resources.
Windows Defender
Windows Defender is a utility that allows you to protect your computer from spyware and other potentially dangerous applications. Here you can also find out when the computer was last scanned, when a scheduled scan will be performed, etc.
Sound
A standard component that was also present in earlier versions of Windows. It allows you to control audio devices connected to your computer. Here you can set up sound schemes, change playback and recording settings, etc. In addition, there is an interesting feature that was not available in previous Windows operating systems - controlling the volume of sounds when you are on audio communication using installed software.
Notification area icons
The notification area is located on the right side of the Taskbar. It is designed to display programs that are automatically loaded when the operating system starts. With the help of the Notification area icons mechanism, you can effectively manage this area by hiding or showing program icons.
You can learn how to customize the notification area in Chapter 8.
Keyboard
This mechanism allows you to control the keyboard and configure many settings. In particular, here you can reduce the delay in the appearance or repetition of characters, increase the cursor blinking speed, etc. Users who are used to working with cursor keys turn to this component in the first place, immediately after installing the operating system. For example, by reducing the character repeat delay time, you can maximize the keyboard's response to cursor keystrokes.
Mouse
This mechanism has not undergone almost any changes since Windows 98. It allows you to control the most used device connected to your computer - the mouse. With it, you can adjust the basic parameters of the manipulator: the speed of the pointer, the speed of double-clicking, the reaction of the scroll wheel, the graphical display of the pointer, etc.
The taskbar and the Start
menu customize the appearance and functionality of the Taskbar and Start menu. For this, this mechanism is used. With it, you can do the following: -
change the location of the Taskbar;
- manage program icons and their grouping;
p to enable or disable the use of preview using Aero Peek;
- customize the appearance and content of the Start menu;
r add or hide the quick launch bar.
The list is far from complete: everything can be configured! You'll learn more about this in Chapter 8.
Indexing Options
Even though Windows 7 is amazing and, one might say, suspiciously fast, you can control what gets indexed and how to access items faster. file system. Using the Indexing Options mechanism, you can add folders for indexing, configure indexing of files and their properties, exclude objects from indexing, etc.
Folder Options
Folders are a file system object that you encounter very often. That is why developers, starting from the very first versions of the operating system, have provided a mechanism with which you can customize the convenience of their use. In Windows 7, this mechanism has received the most advanced and useful features, with the help of which you can not only influence the appearance of the folder and the amount of information displayed by the system about the objects in it, but also customize the way information is searched for in them.
Personalization
For the first time, the concept of personalization appeared in Windows Vista, and the developers of Windows 7 did not abandon it, but only added functionality. Using the Personalization component, you can influence the design of the Desktop, hide or show the main icons that are displayed on it, change the background image, customize themes, change the splash screen, etc.
You can read more about the Personalization component in Chapter 7.
Connecting to remote desktops and RemoteApp applications
With this mechanism, you can influence the remote connections that are used, as well as create new connections. This approach is very convenient because it allows you to manage a remote workstation or access its resources from any computer, such as home.
Getting Started
If you have worked with Windows Vista, then you probably remember which window was loaded when it started. It was an application that in Windows 7 is called Getting Started, which lets you get acquainted with some of the new in Windows 7, as well as in principle important components. These features include transferring data from an old system or computer, creating new Windows user accounts, downloading add-ons, and more.
Programs and Features
Using this mechanism, you can manage software, system components, and service packs installed in the operating system. As a rule, the Programs and Features mechanism is used to remove software, as well as reinstall programs that, for some reason, work with errors. There is also a function with which you can disable or enable some system mechanisms.
Default programs
The Default Programs component allows you to set rules for linking files of different formats to certain programs that will process them. Here you can not only change these applications, but also add other file formats with which they should work. With the help of the same component, you can configure the autorun settings, for which the Autorun component is responsible.
Speech Recognition
An interesting system utility with which you can recognize speech and translate it into text. Unfortunately, only English is supported.
Parental control
The Parental Control mechanism was inherited in Windows 7 from Windows Vista, and its purpose has not changed at all. As before, it can be used to configure permission to use programs and access the Internet for any users whose accounts are registered in the operating system. Since not only adults, but also children can work with a computer, it is quite reasonable for parents to want to prohibit their child from running certain programs and visiting web pages of dubious content. Using Parental Control, you can set not only such restrictions, but also the time of using the computer.
Internet Options
Like previous versions of the operating system, Windows 7 also has a mechanism for configuring the Internet Explorer browser. Using it, you can change many settings that affect the display of information, protection from malicious code, pop-up blocking, and much more. Here you can also set privacy levels, manage add-ons and programs, view certificates, etc. On the other hand, if you do not want to use Internet Explorer and you have an alternative browser, such as Mozilla Firefox, this mechanism will be absolutely useless for you.
System
Several components are collected here at once, with the help of which you can study and configure various parameters that affect the operation of the operating system. So, here you can view basic information about the configuration of the computer, see its performance rating, get information about the identification of the computer, etc. Using this component, you can launch the Task Manager, configure advanced settings and remote access, change identification settings, and much more.
Performance counters and tools
With this mechanism, you can view the performance evaluation of the main hardware - processor, video system, RAM and hard drive. This estimate may vary and depends on the properties of the mentioned devices. Using the Performance Meters and Tools component, you can also configure or run functions that affect the performance of the system as a whole:
□ configure power plans;
□ adjust indexing parameters;
□ customize visual components;
□ run hard disk cleanup;
□ run hard drive defragmentation.
As for performance evaluation, this concept first appeared in Windows Vista. The meaning of this assessment is that any program that can run on a computer has certain requirements for computer resources. These requirements can be interpreted as an assessment. If the rating of the computer's capabilities is lower than the rating required by the program, the latter may refuse to run on the computer in order to avoid possible failures. That is why the higher the score of the computer, the more you can be sure that the desired program will start and work in full force, without experiencing any problems with resources.
Phone and modem
As in previous versions of the operating system, in Windows 7 this mechanism allows you to configure modems installed in the system, set telephone line parameters, add, delete and configure service provider entries, etc.
Color Management The Color
Management mechanism allows you to use the color profiles of connected monitors , printers and other devices that work with graphics. Connecting one or another profile can affect the quality of displaying information or its greater realism when printed, which is often used by computer designers and artists.
Troubleshooting
Using this mechanism, you can solve and fix almost any problems and failures in the operation of hardware or software that are installed and used on your computer. At the same time, all failures and malfunctions are divided into five categories:
□ programs;
□ equipment and sound;
□ network and Internet;
□ design and personalization;
□ system and security.
It is worth noting that the developers of Windows 7 have tried very hard in terms of troubleshooting and resolving problems associated with these malfunctions. As a result, the problem resolution system is very functional and easy to use.
Devices and printers
This mechanism is an improvement on the Printers and Faxes mechanism that was used in previous versions of the Windows operating system. Unlike it, the new mechanism contains data not only about printers and faxes, but also about any other devices connected to the computer. All devices are displayed here, access to which and control of which may affect their operation. These include monitors, external hard drives, external modems, keyboards, mice, scanners, plotters, etc. By double-clicking on the icon of the desired device, you will see the properties window for this device, in which you can configure its settings.
user accounts
A similar tool existed in previous versions of Windows. Its main purpose is to manage user accounts that work on this computer. Here you can create, delete accounts, restrict their rights, set up parental controls, set passwords, etc.
Windows Update
As in previous versions, in Windows 7, using this mechanism, you can manage the system for updating the operating system and installed programs. Here you can search for updates, customize the behavior of the computer when they are found on the official website, view the update installation log, etc. Users who are in doubt or not
If you are sure about some points related to service packs, you can use the link to help information and find out everything that interests them on this issue.
Support Center
A new tool designed to help the user solve various problems. Here you will not only see all the important events that occur in the operating system and require your intervention, but you can also run diagnostics, restore the system after failures, configure virus protection, set user account control settings, etc.
Synchronization Center
With this component, you can synchronize the data of your mobile phone or any other device connected to the computer with the data on the computer. In addition, similar actions can be performed with respect to data stored on the local network. It is thanks to the Sync Center that you can work with offline files without worrying about whether they will be synchronized with respect to the original data. Here you can view sync results and conflicts, set up new sync types, and more. Ease of Access
Center
As with earlier versions of the operating system, developers continue to take care of users who may experience difficulty using the operating system due to problems such as vision or hearing. There are special tools that can make the work of such users easier. You can, for example, increase readable text or even play it with your voice, voice ongoing actions, etc. The Ease of Access Center mechanism is just designed to manage such features.
Network and Sharing Center
Perhaps one of the most important and important mechanisms of the operating system. It connects your computer to the local network and the Internet. Here you can configure settings for network adapters, network services and protocols, settings for sharing resources, troubleshoot network connectivity issues, configure homegroup settings, and much more.
BitLocker Drive Encryption
If you decide that you need to encrypt data, such as those located on a portable USB drive, then this component will take care of everything related to this. You will only have to specify the drive to be encrypted, activate the encryption process and wait for it to finish.
Fonts
The operating system uses a wide variety of fonts in its work. Any software installed on the system can also add its own set of fonts. To have an idea about installed fonts, as well as manage their use in the system, the system Fonts mechanism is used. With it, you can also change font display settings, configure ClearType technology, search for and receive codes for the required characters, etc.
Screen
As in previous versions of the Windows operating system, the Screen component is used to control the monitor screen, namely, to configure the display of information on it.
Here you can change the screen resolution, font size, enable or disable ClearType technology, calibrate color, etc.
With this mechanism, you can create and configure multiple power plans and use them in different situations. For example, you can create one power plan for maximum computer performance, another for maximum energy savings, or another one of your choice. The number of power plans is limited only by your imagination and real needs.
You will learn more about working with this mechanism in Chapter 10.
Regional and Language Options
This mechanism, as in previous versions of the Windows operating system, allows you to select and configure regional standards that affect the display of information such as time, year, currency, etc. In addition, here you can add the desired languages and keyboard layouts, which you would like to use in your work, as well as set the language that will be used when working with programs that do not support Unicode encoding.







 WINDOWS 7 : Customizing Appearance and Workspace
WINDOWS 7 : Customizing Appearance and Workspace